What is Chainlink?
Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network that operates across multiple blockchains simultaneously. Oracles are needed to bring real-world information into smart contracts. Chainlink significantly improves access to oracles, their availability, and accuracy, and has established itself as the standard for cross-chain interoperability.
Table of contents
What problem does Chainlink solve?
Building smart contracts on blockchains presents developers with recurring challenges. Executing contract transactions within a well-defined ecosystem is the least of their problems—after all, that's exactly what blockchain technology was ultimately designed for.

Bitcoin transactions are, at their core, nothing more than highly simplified smart contracts. However, things become more difficult when external factors or data need to be incorporated into contracts. For example, the successful delivery of goods by mail, or the result of a football match that needs to be evaluated for a sports bet. In such cases, so-called oracles are needed: impartial individuals or institutions whose reliability the parties agree upon before concluding a contract.
Additionally, the modern multi-chain landscape creates another problem: blockchains cannot naturally communicate with each other. A smart contract on Ethereum knows nothing about events on Polygon or Avalanche, even though many applications today need to run across multiple chains simultaneously.
Such oracles and the lack of cross-chain communication can sometimes represent vulnerabilities: whether because oracles are biased, unreliable, or simply too expensive, or because cross-chain bridges are insecure and prone to attacks.
The Chainlink platform attempts to address both problems by building a decentralized network for oracle services and cross-chain communication. The developers rely on a multi-chain design that is now available on over 15 different blockchains. Transactions are paid for with the native LINK token.
Chainlink's solution approaches
Chainlink today offers three main categories of services:
1. Data Feeds - Traditional Oracle Services
The original oracle problem is solved through decentralized data feeds that securely make price data, weather data, sports results, and many other external information sources available in smart contracts.
2. CCIP - Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol
The newest and most revolutionary feature enables secure communication between different blockchains—from token transfers to complex multi-chain applications.

3. Additional Services
VRF (Verifiable Random Function) for provably fair random numbers, off-chain computation, and specialized services for traditional financial institutions.
How do Data Feeds work at Chainlink?
Just like the oracles of mythology, who promised seekers knowledge and prophecies by invoking a higher power, oracles in smart contracts serve as reliable, external sources for contract-relevant information. In the case of the football bet described above, implemented in a smart contract, this could be a website that provides game results in machine-readable form. A smart contract can read this information and, depending on it, pay out one of the contract parties after the game ends.
If the stakes aren't too high and the website is trustworthy, this method represents a good way to implement sports betting in a smart contract. Typically, the oracle operator will charge a small fee for providing the information. But what happens when large amounts of money are involved and the possibility of bribing the oracle provider or falsifying the messages becomes more attractive?

In these cases, it's sensible to use information from multiple independent oracles for decision-making. Only when, for example, four different websites unanimously report the outcome of the football match will the contract actually be executed. However, this approach has the disadvantage that selecting and paying for oracles becomes increasingly complex and cost-intensive.
Oracles must generally fulfill three important criteria:
Accuracy of provided data (Integrity)
Service availability (Availability)
Discretion regarding contract contents (Confidentiality)
The complete fulfillment of these requirements is important to enable smart contracts between strangers in the first place. Chainlink solves these challenges through a decentralized network of node operators who can operate simultaneously on multiple blockchains.
Reputation in the Chainlink network
The Chainlink team emphasizes that 100% reliability of an oracle will never be achievable. Even the most reliable provider is always at risk of being hacked or compromised in some other way. Therefore, it's important for most smart contracts to rely on multiple oracles that ideally derive their knowledge from different sources.
Chainlink captures, for example, the time individual oracles need to announce a specific event. The longer a provider takes to notify an event, the worse their availability rating becomes.
The assessment of data integrity works similarly. When there's more than one oracle for an event, it's quick and easy to identify whether one of the sources deviates from the majority of others. This way, each oracle receives a score that informs about the provider's reliability.
The Chainlink network now secures over $18 trillion in transaction volume—proof of the industry's trust in this infrastructure.
CCIP - Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol
One of Chainlink's most important innovations is the Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP), which launched in July 2023 and has been available to all developers since April 2024. CCIP solves a fundamental problem of the blockchain landscape: the inability of different chains to communicate securely with each other.
What makes CCIP special?
Unlike conventional cross-chain bridges, which often have security issues and are regularly hacked, CCIP offers "Level-5 Security" through a three-layer security architecture:
Multiple independent oracle networks verify every cross-chain transaction
Risk Management Network monitors all transactions in real-time
Anti-Fraud Network automatically detects and stops suspicious activities
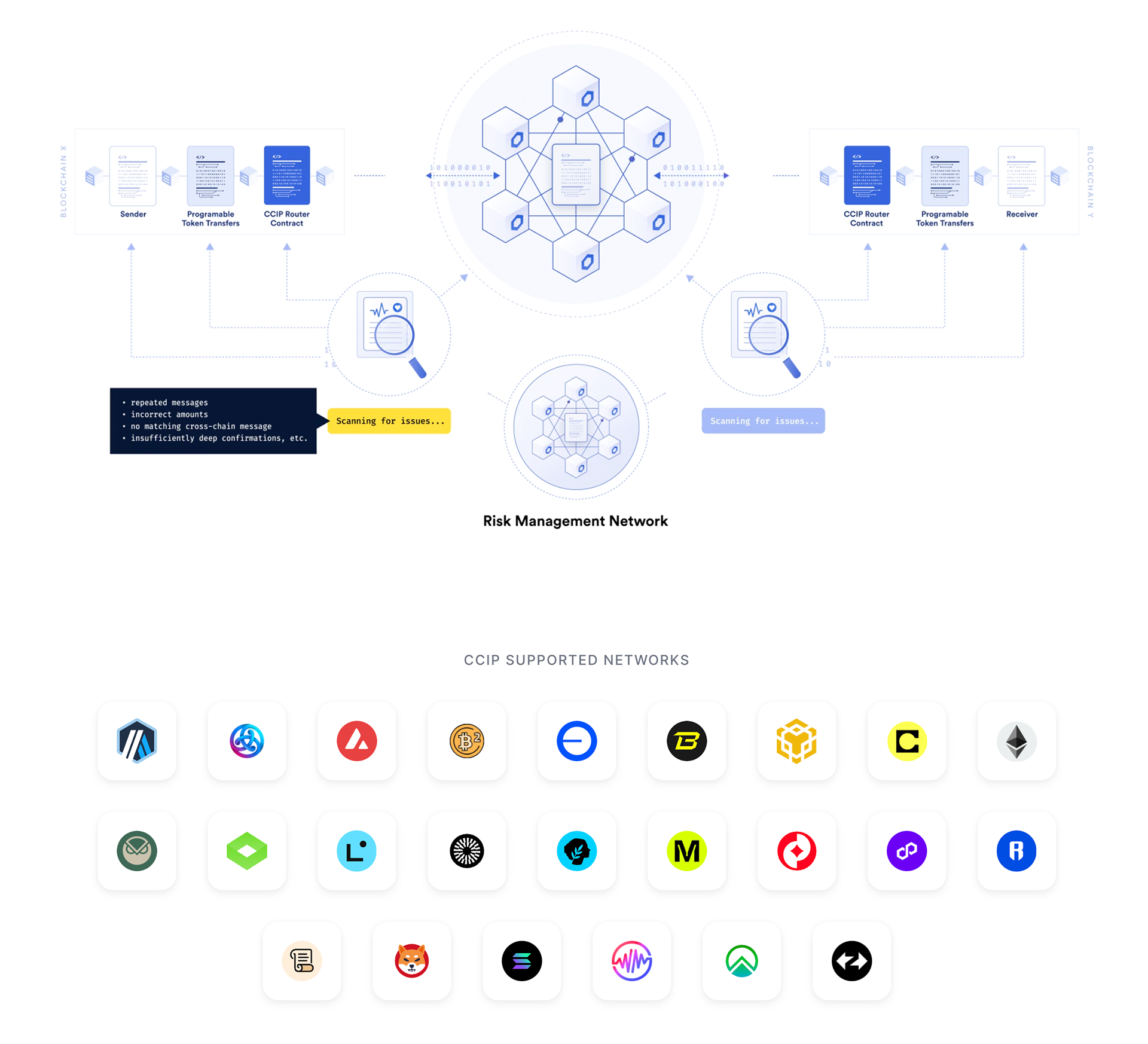
CCIP Functionalities
CCIP enables three main functions:
Arbitrary Messaging: Sending encoded data to smart contracts on other blockchains. Developers can build complex multi-chain applications with this.
Token Transfer: Secure transfer of tokens between different chains, either through lock/mint or burn/mint mechanisms.
Programmable Token Transfer: Combination of token transfer and messaging—tokens are transferred while simultaneously transmitting instructions on what should happen with them.
Supported Blockchains
CCIP is currently available on the following chains:
Ethereum
Arbitrum
Avalanche
Base
BNB Chain
Kroma
Optimism
Polygon
WEMIX
Additional chains are continuously being added.
Use Cases for CCIP
Cross-Chain DeFi: Users can move liquidity between different DeFi protocols on various chains to find the best interest rates.
Cross-Chain Lending: Deposit collateral on one chain and take out loans on another chain.
Cross-Chain Gaming: Web3 games can function across chains, allowing players on different chains to compete against each other.
Omnichain Applications: Applications that work seamlessly across multiple chains simultaneously, without users noticing the underlying complexity.
Additional Chainlink Services
VRF - Verifiable Random Function
Chainlink VRF delivers provably fair random numbers for blockchain applications. This is particularly important for gaming, NFT generation, and lotteries where fairness is crucial.
Automation
Chainlink Keeper (now Automation) automatically executes smart contract functions based on predefined conditions—without human intervention.
Integration with traditional financial institutions
Chainlink works with major financial institutions like Swift to connect traditional banking systems with blockchain technology. These partnerships pave the way for tokenized Real-World Assets (RWAs) worth an estimated $500 trillion.
Potential and opportunities of Chainlink
The lack of decentralized infrastructure for oracle mediation and cross-chain communication was long one of the biggest barriers to blockchain adoption. Chainlink has established itself as the de facto standard and today secures more value than any other oracle solution.
With CCIP, Chainlink positions itself as a central building block for the "Internet of Blockchains"—a future where different chains work together seamlessly. Integration with traditional financial institutions through projects like Swift shows that Chainlink is gaining importance outside the pure crypto world as well.
Smart contracts are important, among other things, for enabling payments between users of different blockchains. An efficient and reliable market for oracles and cross-chain services has the potential to significantly increase permeability and compatibility between different cryptocurrencies.
The continuous development of new services and expansion to additional blockchains makes Chainlink one of the most promising infrastructure projects in the entire blockchain ecosystem. With over 1,000 integrated projects and support from both DeFi protocols and traditional financial institutions, Chainlink is well-positioned to continue playing a central role in the future.
Frequently asked questions about Chainlink
What is the current price of Chainlink?
The current price of Chainlink is $9.08. Over the past 24 hours, the price is up 3.64%, with a trading volume of $56.04B. Chainlink is the 18th largest cryptocurrency by market cap, currently at $6.44B.
Is it worth investing in Chainlink?
The price change of Chainlink (LINK) over one year is currently -52.77%, making Chainlink a bad investment in hindsight. Whether this trend will continue in the future depends on many external factors such as supply and demand. Past price trends are no indicator of future performance.
Where can I buy Chainlink?
The best and most reputable crypto exchanges for buying Chainlink include ones such as Kraken and Coinbase. You can find more in our comparison of crypto exchanges.
Which Chainlink wallet is the best?
The best hardware wallets for Chainlink are Ledger Nano X, BitBox02 and Trezor Model T. In our opinion, the best software wallet for Chainlink is the Zengo app. You can find more in our comparison of crypto wallets.
What was the all-time high of Chainlink?
The Chainlink (LINK) cryptocurrency all-time high is $52.70. This price was reached on May 10, 2021. The current price is $9.08, a difference of -82.76% from the all-time high.
Who has invested in Chainlink?
Chainlink's early investors include institutional investors and venture capitalists (VCs) such as 8Decimal, Anmi OECD, Consensus Capital, Framework Ventures, Outlier Ventures, Fundamental Labs.
How many Chainlink (LINK) are currently in circulation?
There are currently 708.1M Chainlink (LINK) in circulation. The total amount of LINK in circulation represents all coins and tokens that have already been distributed and are therefore held in the wallets of private individuals, companies or institutions.
How many active addresses (24h) does Chainlink have?
As of the last update, Chainlink had about 4,782 active addresses (24h) — the number of unique addresses that sent or received a transaction in a rolling 24-hour window (each address counted once). Note: addresses ≠ users (one person or an exchange can control many).
How many transactions per day are running on Chainlink?
Chainlink currently has an average of around 10,799 transactions per day. This key figure indicates how many network transactions have taken place on average per day in the last 3 months.